MBC101 - What Happens When MBC Spreads to the Brain?
Why is CNS metastasis from breast cancer so challenging to treat?
The short answer: Blood Brain Barrier
So we know that BBB is a network of vessels and tissue that keeps the space very close, so that harmful substances cannot be a threat to the brain because the brain is our moral vital organ. So we don't want any harmful substances or toxins or bacteria or viruses to get into that space. So it's very tightly connected tissue network that allows normal substances such as water, and sugar. and carbon dioxide, things that our cells need, to pass by. But any bigger substances like bacteria or drugs cannot not penetrate and cause more harm. However, in patients that have brain metastases, as we mentioned before, sometimes when we do radiation, we open a space into the blood brain barrier and some of those drugs can actually penetrate and that will help the treatment. (Transcript, Dr. Soyano)
Brain Radiation Treatments
“A big shift toward SRS has taken place over the past decade, which largely has been driven by the results of several randomized trials, specifically those reported by Soffietti and colleagues, Aoyama and colleagues, and Chang and colleagues. In these trials, patients with up to 3 or 4 brain lesions underwent SRS either alone or in combination with whole-brain radiation. All of the studies showed that although the addition of whole-brain radiation delayed progression to the next central nervous system (CNS) event, overall survival did not improve, quality of life worsened, and neurocognitive problems developed. So for patients who present with a limited number of lesions that are small enough and in a location amenable to SRS, we use that approach in an attempt to minimize short- and long-term toxicity to the brain. Patients who present with multiple lesions, however, are still best served by whole-brain radiation.” (Dr. Nancy Lin Update on Managing Brain Metastases in Breast Cancer)
-
Fatigue
Scalp irritation
Hair loss
Nausea, vomiting
Headaches
Muffled hearing
-
Short term memory loss (whole brain radiation therapy)
Damage to normal tissue (very rare)
-
Blood brain barrier (BBB) can pose a challenge to entry of drugs into the central nervous system (CNS)
Studies suggest opening of blood BBB with receipt of whole brain radiation (WBR) therapy or stereotactic radiation (SRS) therapy
Optimal window may be in 1 month post treatment
Ionizing radiation is a form of energy that acts by removing electrons from atoms and molecules of materials that include air, water, and living tissue. Ionizing radiation can travel unseen and pass through these materials.
What are the best ways to reduce the risk for cognitive side effects from whole-brain radiotherapy?
“The 2 main ways to reduce the risk for cognitive side effects from whole-brain radiotherapy are medication and alteration of the radiation treatment field. Memantine is the agent that has been most studied for this use. For example, the phase 3 RTOG (Radiation Therapy Oncology Group) 0614 trial by Brown and colleagues compared memantine vs placebo for prevention of cognitive dysfunction in patients receiving whole-brain radiation. Like most trials with radiation, this study enrolled mostly patients with non–small cell lung cancer; only a fraction of the patients had a primary diagnosis of breast cancer. The researchers showed that at 24 weeks, the patients taking memantine had less cognitive decline than those taking placebo. The study was somewhat underpowered because the patients had poorer survival than expected; fewer patients were alive for assessment at the 24-week point than had been projected. Ultimately, however, whether the differences were statistically significant or simply trends, all of the endpoints measured favored memantine. As a result, many practitioners are routinely using memantine with whole-brain radiation.
The other approach to reducing cognitive side effects in whole-brain radiotherapy is the use of hippocampus-sparing techniques. In a single-arm trial conducted within the RTOG, in which a hippocampus-sparing approach to whole-brain radiotherapy was used, cognitive function was fairly stable at 4 and 6 months, the points at which cognitive function typically worsens with standard whole-brain therapy. Of course, despite the encouraging results, this was a nonrandomized study—we do not know whether the apparent difference was simply due to chance or patient selection. In an ongoing phase 3 study from NRG Oncology, NRG-CC001 (A Randomized Phase III Trial of Memantine and Whole-Brain Radiotherapy With or Without Hippocampal Avoidance in Patients With Brain Metastases; NCT02360215), all patients receive memantine and are randomly assigned to either standard or hippocampus-sparing whole-brain radiotherapy.”(Dr. Nancy Lin Update on Managing Brain Metastases in Breast Cancer)
Immunotherapy in Combination with Radiotherapy
A recent trial on atezolizumab on advanced and metastatic TNBC did not show a significant benefit in patients with brain mets. Despite these results, several clinical trials are now evaluating the role of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), such as nivolumab (NCT03807765), pembrolizumab (NCT03449238) and atezolizumab (NCT03483012), in combination with SRS in brain mets from TNBC. Recently, a single-arm, phase 2 study of pembrolizumab in 20 patients with from solid tumors (17 BC, 2 NSCLC and 1 ovarian cancer) showed promising results. . Further analyses are ongoing to identify subgroups of patients that may benefit from anti PDL-1 treatment
“We are very interested in bringing immunotherapy to the brain metastasis space in breast cancer. We know that immunotherapy has activity in brain metastases from lung cancer and melanoma, and we want to see if the same is true in breast cancer. The breast cancer trials to date have generally excluded patients with brain metastases. We have a trial looking at HER2-directed therapy plus atezolizumab (Tecentriq, Genentech) for HER2-positive breast cancer, and we also have a study looking at SRS plus atezolizumab in patients with triple-negative breast cancer and brain metastasis (NCT03483012).
Dana-Farber, in collaboration with the Translational Breast Cancer Research Consortium (TBCRC), is also studying the use of neratinib plus capecitabine in HER2-positive breast cancer with brain metastases (NCT01494662), and later this year, a new arm will be added to this study in which neratinib will be combined with TDM-1. We also hope to open a number of additional studies over the next year based on our preclinical work; these studies may include work looking at brain-permeable phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors, and at CDK4/6 inhibitor–based combinations.
HER2+ Leptomeningeal Disease
Our brain and spinal cord are protected by three layers of tissue called meninges. Between two of the layers is cerebrospinal fluid, or CSF, in a place called the intrathecal space. That’s why cancer-fighting drugs placed into this space are called intrathecal chemo drugs or IT chemo.
One way to get this treatment is with a lumbar puncture, or spinal tap. Herceptin is given over a long period and many doses, lumbar puncture does not cut it., so a different delivery mechanism is generally used.. This is a small dome-shaped device called an Ommaya reservoir. It’s placed under patient’s scalp during a short surgery. It has a catheter that connects to the intrathecal space. Getting treatment this way is like getting it through an IV port elsewhere in the body
Trastuzumab or Herceptin has revolutionized the outcome of patients with HER-2 overexpressing breast cancer. Traditionally, HER-2 overexpressing tumors have been associated with more aggressive disease and inferior prognosis, , trastuzumab has transformed HER-2+ breast cancer into one of the most treatable types of cancer Trastuzumab’s control of systemic disease in HER-2+ breast cancer patients has led to a higher incidence of CNS metastases HER-2+ metastases can develop in areas where intravenous (IV) trastuzumab has little to no penetration, particularly the central nervous system (CNS) where brain and leptomeningeal (LM) metastases can occur. The development of this complication warrants a multi-faceted approach. . As trastuzumab is highly effective against systemic HER-2+ breast cancer, a logical strategy is to target HER-2+ CNS metastases directly
Ongoing Clinical Trials H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute
Radiation Therapy Followed by Intrathecal Trastuzumab/Pertuzumab in HER2+ Breast Leptomeningeal Disease (NCT04588545) Phase 1/2
Systemic Therapies
“Not all breast cancers are the same, not all breast cancers are developed or found because of the same cancer markers.
So we tend to divide them into different subtypes. And those subtypes are based on the three main receptors that we can find in breast cancers, which are the estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and the HER2 receptor. So when either the estrogen or the progesterone is overexpressed in breast cancer, we call that hormone positive breast cancer. And what that means is that the breast cancer cells are feeding off of the hormones: estrogen, or progesterone. They use them as a food or fuel to live. The HER2 receptor acts differently when it's overexpressed, it just allows the breast cancer cells to grow rapidly.
So the most common subtype of breast cancer in the U S is hormone positive/HER2 negative and represents about a 70% of those breast cancer cases. The other 30% is represented between the triple negative and the hormone positive. And there's also a different molecular subtyping, called Luminal A, Luminal B, basal-like, and HErR2-like. There is a lot of overlap, but it tells us mainly that for those hormone positives, there are ones that have a little bit better prognosis and responsiveness to hormonal treatments and other ones that are less responsive to hormonal treatments, but responsive to chemotherapy.” (Transcript, Dr. Soyano)
“We know that patients are living longer, and breast cancer is a second most common cancer in the U S in females after skin cancers, and we're detecting it earlier.
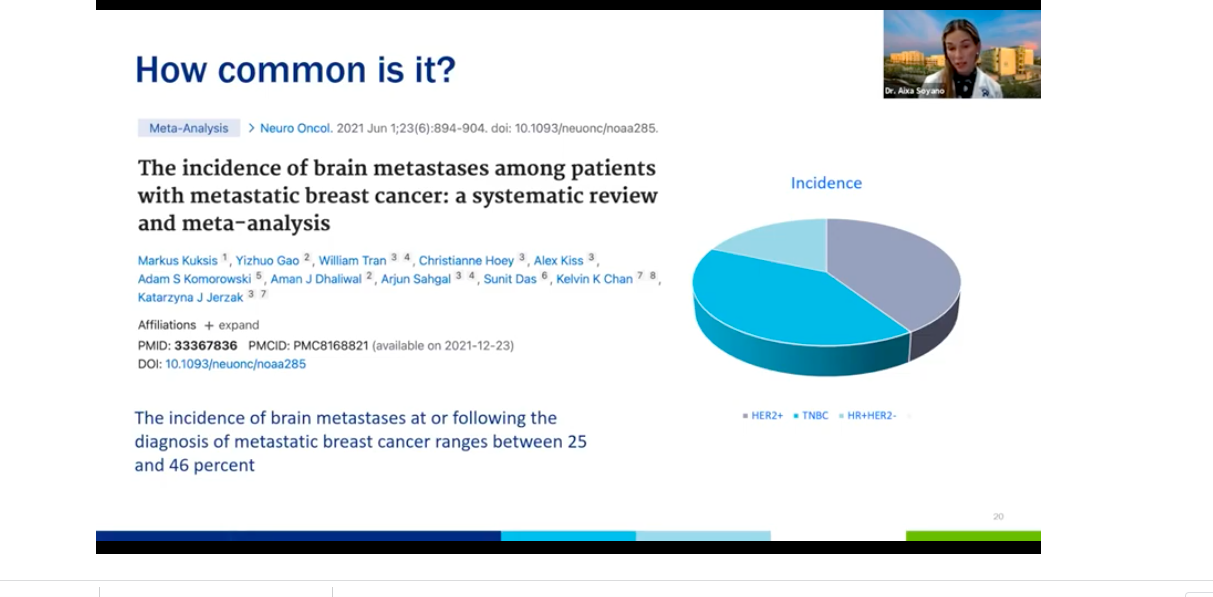
The incidents of brain metastases seems to be going up as well. A meta analysis (a collection of other trials) that was published this year showed that the incidents of brain metastases following the diagnosis of metastatic breast cancer ranges are between 25 and 46%.
So somewhere along the 20 to 40% of breast cancer patients that have metastases will develop metastases to the brain. We also know that the hormone HER2 negative was the most common subtype of breast cancer found in early state, but this is not true for breast cancer brain metastases.
The most common ones are the HER2 positive and the triple negatives. And that represents a little bit over a third of those. And then only about 15% of the breast cancer brain metastases are hormone positive/HER2 negative. Hereat our institution we did a retrospective review of all the brain metastases that were found in our database of breast cancer, lung cancer, melanoma. We found that because there's no real screening national guidelines looking for brain metastases in breast cancer patients, the patients that had breast cancer were more likely to be younger with more advanced central nervous system disease, require whole brain radiation and have poor overall survival in general, compared to the lung cancer patients and the melanoma patients.
So it's food for thought about modifying and trying to find these patients earlier so that their outcome can be improved in the future(Transcript, Dr. Soyano)
The most common subtype of breast cancer. It tends to be more indolent, and the patients tend to have a longer life expectancy. Common sites of metastases include the bones, lungs, and the liver. Initial treatment options include endocrine therapy, which we call hormone blockers plus or minus targeted therapy, which could be CDK4/6 inhibitors or mTOR inhibitors.
These are inhibitors of particular areas of the cell cycle. So if we are inhibiting division of the cells, the cells get arrested, and they cannot further progress. (Transcript, Dr. Soyano)
Ww know that CDK4/6 inhibitors, especially Ibrance and Verzenio have shown some intracranial activity in small early phase trials. So it gives us an idea that this drugs potentially can penetrate that BBBB and help treat. the brain mets in combination with the local regional therapies. There was also a phase 2 trial of hormone positive metastatic patients with active brain metastases that showed a modest clinical benefit.
It was a small trial, and even though they did not meet what their primary endpoint, it included a variety of patients with more advanced unresectable tumors, lepto mets, etc.
But importantly, the blood study from the patients on this trial showed that there were adequate concentrations of the drug that suggests that there was a good penetrance of this drug. So that led us to study that here at Moffitt cancer center, Dr.Ahmed is the PI.
So we have a Phase 1/2 study of stereotactic radiation or SRS in the management of patients that are HR+/HER2- with brain metastases. So this trial allows patients that are eligible for SRS. That have up to 15 brain meds.
They will be getting Verzenio with radiation in the beginning continuing with Verzenio along and will be followed up by their response. This trial is recruiting at Moffitt.
Additionally, at Emory University in Atlanta, there's a similar study using stereotactic radio surgery with any CDK4/6 inhibitor in treating this patient.
So another investigator is looking at that same concept, hopefully we'll have more data so we can, , change practice for the future. (Transcript, Dr Soyano)
A different subtype of breast cancer is called triple negative. It lacks expression of estrogen, progesterone or the HER2 receptors, these cancers tend to be more aggressive and are associated with genetic mutations or predisposition, such as BRCA1/2 mutations among others.
Patients are commonly treated with chemotherapy plus or minus a combination with immunotherapy.
The most common site of metastasis are liver, lung, and brain. And because we treat these patients commonly with chemotherapy, we know from experience that some chemotherapy agents penetrate the blood brain barrier to some degree. (Transcript, Dr. Soyano)
The first antibody drug conjugate (ADC) approved by the FDA last year in April. It's an antibody that goes in and targets a specific protein present in cancer cells. For this particular drug, the protein is called Trop2.
And that antibody is linked to a small chemotherapy drug. That drug is called SN38, so when the medication is administered, it targets the Trop2 proteins in the breast cancer cells and delivers the chemotherapy SN 38 directly into the cells.
And that inhibits the repair of DNA and leads to cell death. Approval was based on the results from a trial called the IMMU-132-01. There was another trial called the ASCENT 3 that showed that in some patients that had breast cancer brain metastases, there was an improvement in the progression free survival or the time to progression in patients that had stable brain metastasis from their tumors.
Want more?
Check out the new Breast Cancer Brain Mets website - to find a comprehensive repository of resources, clinical trials, and insights from fellow patients.